content

We often come across various jargons when referring to a spec sheet of an electric two-wheeler. There are figures with a ‘kW’ (kilo Watt) alongside them, and for those who aren’t aware, it’s the power dished out from the bike/scooter’s motor. Now speaking of motors, there are quite a few different setups that manufacturers use as per the need of their product. In this story, we’ve listed and briefly explained various types of drives/motors used in electric two-wheelers.
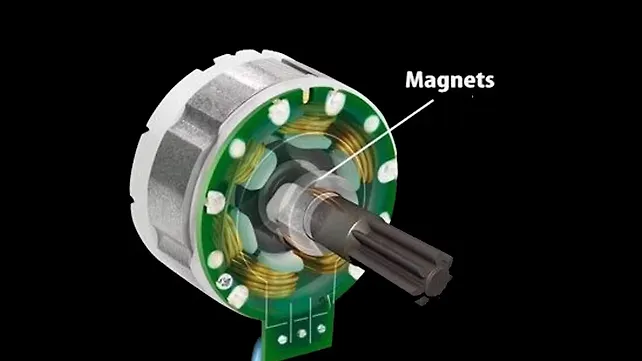
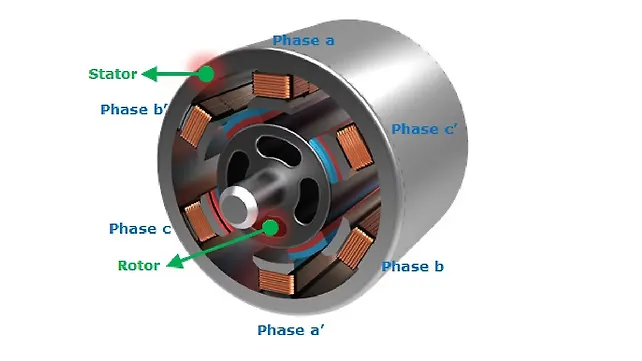
Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor

A Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor or PMSM is the most modern motor used for an electric two-wheeler. It’s an AC synchronous motor and is used for a higher efficiency application in an EV. Its functioning depends on the stator's rotating magnetic field and the rotor's constant magnetic field. While it’s similar to the BLDC motor, the PMSM uses alternating current and also produces notably more torque. A lot of modern electric two-wheelers currently on sale in India use a PMSM.
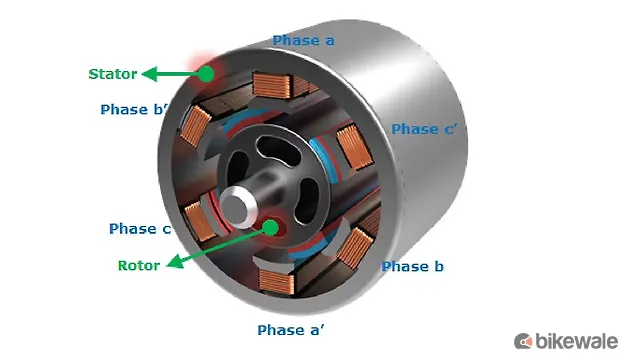
Brushless DC Motor

The Brushless DC Motor (BLDC) is a tad older than the PMSM but is still in application on a lot of EVs. It uses a permanent magnet that works in tandem with a stator coil. The DC power energises this coil and turns it into an electric magnet. A BLDC motor is more sustainable than its predecessor and achieves a higher top speed. However, it’s costly to manufacture compared to a Brushed DC Motor.
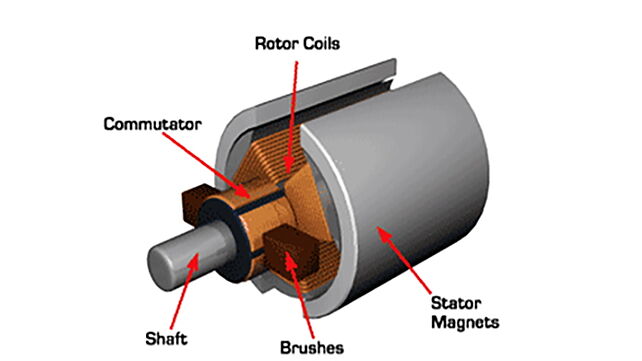
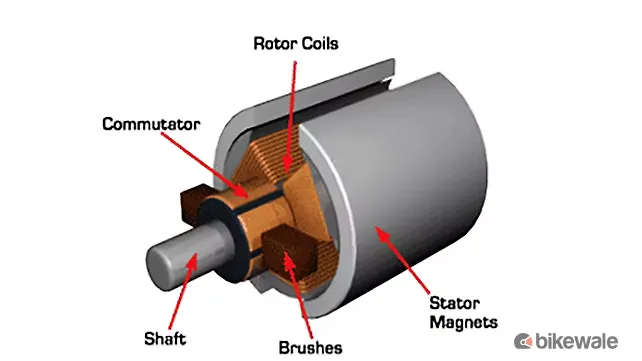
Brushed DC Motor

The Brushed DC motor is the oldest of the lot and its existence dates back to about a century. The construction of a Brushed DC motor includes brushes that work with a permanent magnet. However, with constant friction caused by rubbing against the magnets, the units wear out and need to be replaced. Moreover, the Brushed DC Motor is notably less efficient and also creates noise, which reduces its preference amongst various machines.
Gallery
1/4
OLA S1 Front View
Double Tap to Zoom